In the world of pest control, understanding the chemicals at our disposal is crucial. One such insecticide, bifenthrin, has gained attention for its effectiveness against various insects. But a common question arises, what insects does bifenthrin kills or target?
As a synthetic pyrethroid, bifenthrin offers a unique approach to managing pests. Its ability to disrupt the nervous systems of insects makes it a popular choice among farmers and homeowners alike. However, its impact extends beyond just the intended targets.
With concerns about environmental safety and non-target species, it's essential to explore the full scope of bifenthrin's effects.
Join us as we uncover the fascinating world of what insects bifenthrin kills, exploring its role in pest management and the implications for our environment.
Table of Contents
ToggleBifenthrin Overview
Bifenthrin is a synthetic pyrethroid insecticide widely used in agriculture and pest control. It is particularly effective against a variety of insect pests, including ants, aphids, termites, and many others.
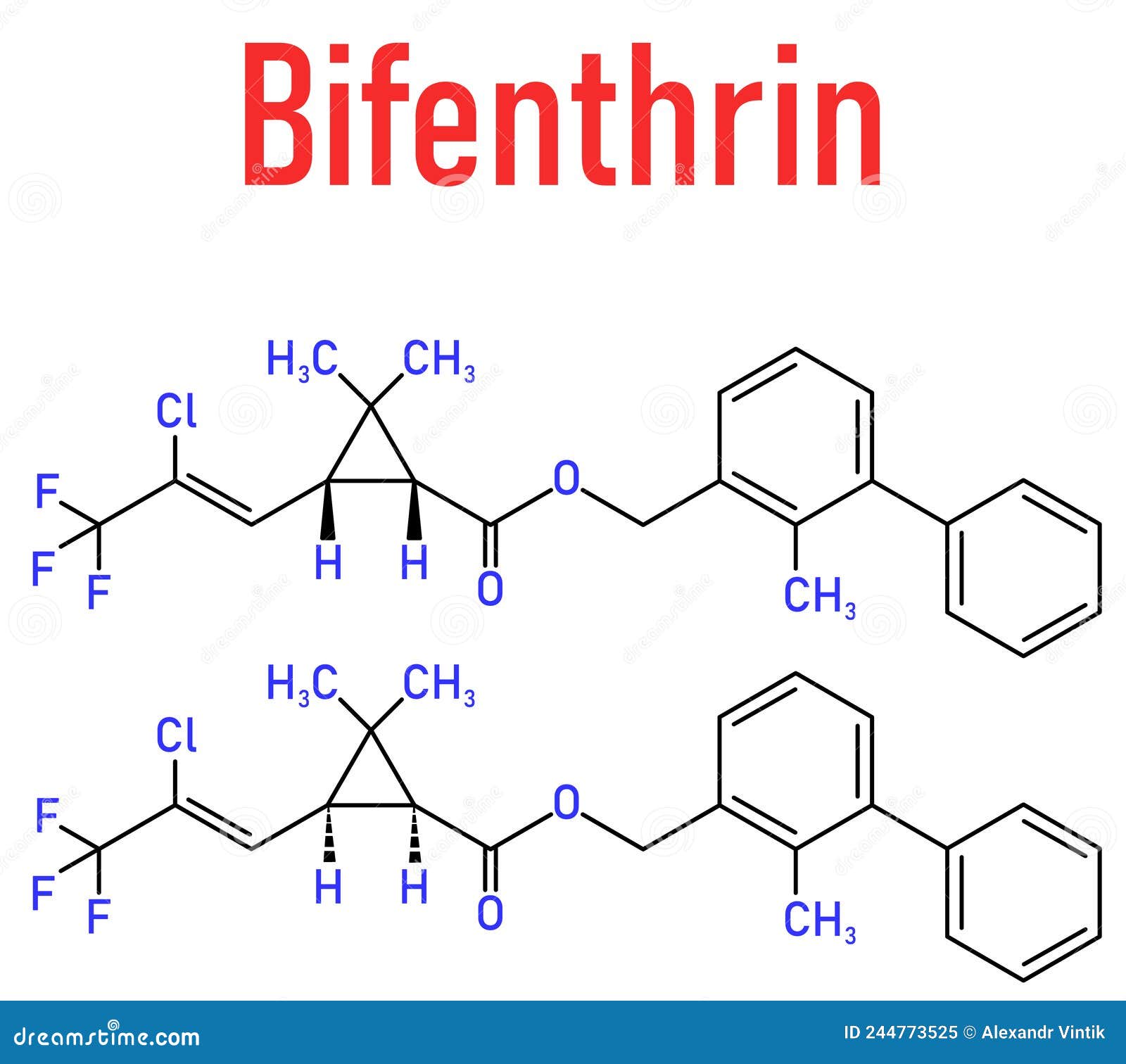
Chemical Properties
- Chemical Structure: Bifenthrin is a chiral molecule, primarily existing as two enantiomers: 1S-cis-bifenthrin (more toxic) and 1R-cis-bifenthrin. Its molecular formula is
C23H22ClF3O2with a molecular weight of approximately 422.9 g/mol. - Physical State: It appears as a white, waxy solid with a faint sweet odor and has low solubility in water, approximately 0.1 mg/L.
- Persistence: Bifenthrin has a long residual life in soil, ranging from 7 days to 8 months, depending on soil type. It tends to bind tightly to soil particles and organic materials, reducing its mobility.
Applications
- Agriculture: It controls a range of pests on crops such as bananas, apples, and ornamental plants.
- Urban Pest Control: It is effective against household pests like ants, spiders, and termites.
- Formulations: Available in multiple forms including emulsifiable concentrates (EC), granules, and powders.
Safety and Toxicity
- Toxicity Levels: Bifenthrin exhibits high toxicity to aquatic organisms and moderate toxicity to mammals. The acute oral LD50 for mice is about 43 mg/kg, indicating significant risk upon ingestion. Symptoms in humans may include skin irritation and respiratory issues if inhaled or absorbed through the skin.
- Environmental Impact: Due to its hydrophobic nature, bifenthrin is less likely to contaminate groundwater but can accumulate in sediments and affect aquatic life adversely. Fish are particularly sensitive due to their slower metabolism.
- Regulatory Status: Bifenthrin is classified by the U.S. EPA as a possible human carcinogen (Category C) and has faced scrutiny regarding its safety for residential use due to its toxicity profile.
In summary, bifenthrin is an effective insecticide with significant applications in agriculture and pest control but poses risks to both human health and the environment that warrant careful handling and regulation.
Working Mechanism of Bifenthrin
How Bifenthrin Works>
Bifenthrin operates primarily by targeting the nervous system of insects. It binds to voltage-gated sodium channels, disrupting normal nerve function. This action leads to prolonged depolarization, causing paralysis and ultimately death in the affected pests.
Neurotoxic Effects
The neurotoxic effects of bifenthrin are significant. When insects come into contact with this insecticide, their ability to transmit nerve impulses is severely impaired. This results in a rapid decline in their motor functions.
Comparison with Other Insecticides
When comparing bifenthrin to other insecticides, it stands out for its potency. While many insecticides target similar pathways, bifenthrin's unique binding properties make it particularly effective against a wide range of pests.
- Pyrethroids: Similar in action but vary in effectiveness and safety profiles.
- Neonicotinoids: Target different receptors but have raised concerns about environmental impact.
- Organophosphates: Older class with broader toxicity but less targeted action.
Understanding these differences helps users choose the right product for their pest control needs while considering both efficacy and safety.
What Insects Does Bifenthrin Kill?
Common Insects Targeted
Bifenthrin is effective against a variety of pests, making it a versatile option for both agricultural and residential use. Here are some of the most common insects it targets:
- Mosquitoes: Particularly effective against species that transmit diseases.
- Ants: Effective in controlling various ant species, including red fire ants.
- Beetles: Targets pests like Japanese beetles that damage crops.
- Moths and Caterpillars: Controls pests such as corn earworms and other larvae.
Efficacy Against Specific Pests
The effectiveness of bifenthrin can vary depending on the pest species. Some insects, like certain mosquitoes, may develop resistance over time, making ongoing research essential for effective pest management strategies.
Understanding which insects are susceptible to bifenthrin helps users apply this insecticide effectively, ensuring better control over pest populations while minimizing environmental impact.

What Insects Does Bifenthrin Kill For Agricultural Use?
Bifenthrin is a widely used pyrethroid insecticide in agriculture, known for its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of insect pests. Below is a detailed overview of the insects that bifenthrin targets in agricultural settings.
Bifenthrin is effective against various insect groups, including:
Chewing Insects
- Bollworms
- Caterpillars
- Cutworms
- Armyworms
- Leaf folders
Sucking Insects
- Aphids
- Whiteflies
- Leafhoppers
- Thrips
Other Pests
- Ants (including red fire ants)
- Termites
- Cockroaches
- Spiders
- Mites (e.g., clover and spruce mites)
- Beetles (e.g., flea beetles, elm leaf beetles)
- Gnats and Midges
- Ticks and other arachnids
What Bugs Does Bifen IT Kill?

Bifen IT is a broad-spectrum insecticide that contains bifenthrin as its active ingredient. It is effective against a wide variety of pests, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor use. Here’s a summary of the key pests that Bifen IT can kill:
The product is noted for its residual effectiveness, lasting up to several weeks depending on environmental conditions and application method.
Pests Targeted by Bifen IT
- Ants: Includes carpenter ants and Argentine ants.
- Aphids: Effective against various species, including greenbugs.
- Caterpillars: Targets several types such as armyworms and cutworms.
- Beetles: Includes flea beetles, elm leaf beetles, and black turf ataenius.
- Fleas and Ticks: Provides control for fleas and various tick species (e.g., brown dog ticks, deer ticks).
- Mosquitoes: Effective in reducing mosquito populations, including those that carry diseases.
- Spiders: Non-poisonous spiders are also affected.
- Other Insects: Includes crickets, earwigs, grasshoppers, mealybugs, moths (like gypsy moths), and wasps.
Additional Details
Bifen IT can be used in various settings such as:
- Around home foundations, porches, and patios to prevent pest entry.
- On lawns, ornamental plants, and vegetable gardens to protect against infestations.
- In commercial and industrial buildings for pest control.
Environmental Impact
Effects on Non-target Species
While bifenthrin is effective against many pests, it can also pose risks to non-target species. Its neurotoxic properties can affect beneficial insects and other wildlife, raising concerns about its broader ecological impact.
- Bees: Exposure to bifenthrin can harm bee populations, crucial for pollination.
- Aquatic Life: Runoff can lead to toxicity in fish and invertebrates, disrupting aquatic ecosystems.
- Birds: Indirect effects may occur through the food chain, impacting birds that consume affected insects.
Residual Effects in Soil and Water
The persistence of bifenthrin in the environment is another important consideration. It can remain in soil and water systems for extended periods, potentially leading to accumulation and long-term ecological consequences.
Understanding these impacts is vital for responsible use, ensuring that while we manage pest populations effectively, we also protect the surrounding ecosystem.
Safety Considerations With Bifenthrin
Human Exposure Risks
While bifenthrin is effective in pest control, it is essential to consider the potential risks associated with human exposure. Proper handling and application are crucial to minimize health hazards.
- Dermal Exposure: Contact with skin can lead to irritation or allergic reactions.
- Inhalation: Breathing in aerosolized bifenthrin may cause respiratory issues.
- Ingestion: Accidental ingestion can pose serious health risks, especially to children and pets.
Regulatory Status
The regulatory status of bifenthrin is important for users to understand. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has classified it as a possible human carcinogen, which underscores the need for caution during its use.
Awareness of these safety considerations helps ensure that bifenthrin is used responsibly, balancing effective pest management with the protection of human health and safety.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Agricultural Use in Crop Protection
In agricultural settings, bifenthrin has been used effectively to manage pests like aphids in corn production. Farmers have reported significant reductions in pest populations, leading to improved crop yields and healthier plants.
Impact on Crop Yields
The application of bifenthrin not only controls pests but also enhances the overall health of crops. This results in higher quality produce and increased profitability for farmers.
Case Study 2: Urban Pest Control
In urban environments, bifenthrin is commonly used for termite control. Its effectiveness against these destructive pests has made it a preferred choice among pest control professionals.
- Long-lasting Protection: Bifenthrin provides residual protection, preventing future infestations.
- Targeted Application: Its use in localized areas minimizes environmental impact.
Case Study 3: Vector Control Programs
In public health initiatives, bifenthrin is employed in vector control programs aimed at reducing mosquito populations. This is particularly important in areas prone to diseases like malaria and dengue fever.
The strategic application of bifenthrin in these programs has led to a decrease in mosquito-borne illnesses, showcasing its role in protecting community health.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
In summary, bifenthrin is a powerful insecticide that effectively targets a wide range of pests, including mosquitoes, ants, and beetles. Its mechanism of action disrupts the nervous systems of these insects, leading to their control.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
While effective, it is crucial to consider the environmental impact and potential risks to non-target species. Understanding these factors helps users apply bifenthrin responsibly and safely.
Future Outlook on Bifenthrin Use
The future of bifenthrin in pest management will likely involve ongoing research into resistance management and environmental safety. As pest populations evolve, adapting our strategies will be essential for sustainable pest control.
By staying informed about the benefits and challenges associated with bifenthrin, users can make educated decisions that balance effective pest management with ecological responsibility.